A prolonged exposure to UV radiation may have adverse effects on the health of human beings, such as for the skin, the eyes and the immune system.
Excessive exposure to UV radiation, in the short term, may produce changes in cellular components on skin, fibrous tissue and blood vessels, leading to a premature skin aging, even in the worst case, a deadly cancer. UV radiation may also cause inflammatory reactions in the eyes, such as actinic keratitis.
The biological effects produced by overexposure to UV radiation may cause serious damages to plant systems due to the alteration of chlorophyll, giving rise to the reduction of crops.
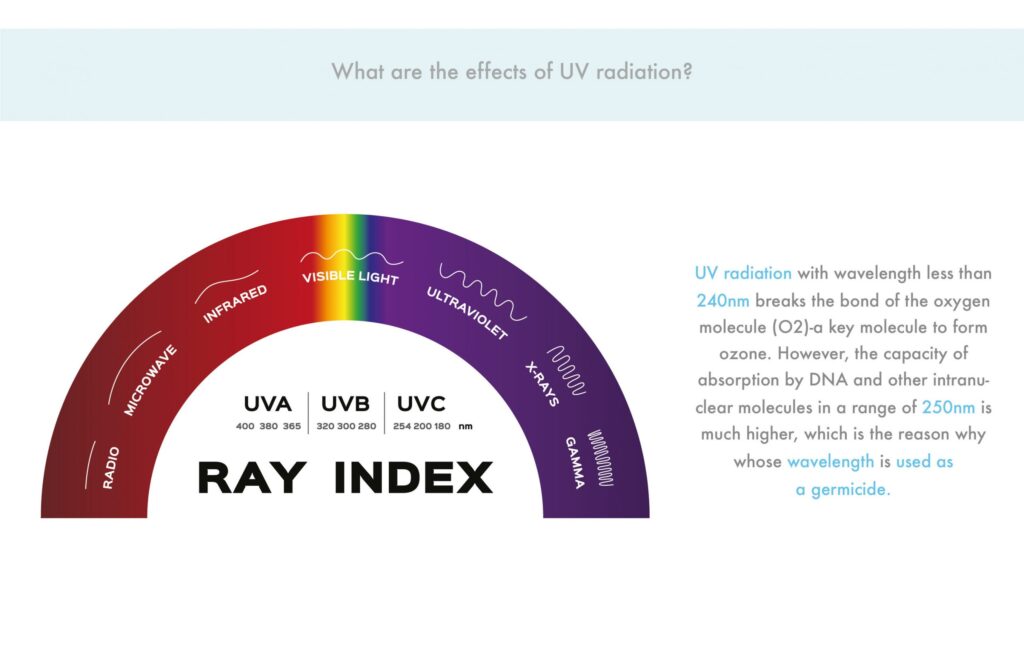
It exists a correspondence between the UV photon energy and the binding energy of many chemical and biological molecules.
UV radiation with wavelength less than 240nm breaks the bond of the oxygen molecule (O2)-a key molecule to form ozone. However, the capacity of absorption by DNA and other intranuclear molecules in a range of 250nm is much higher, which is the reason why whose wavelength is used as a germicide.
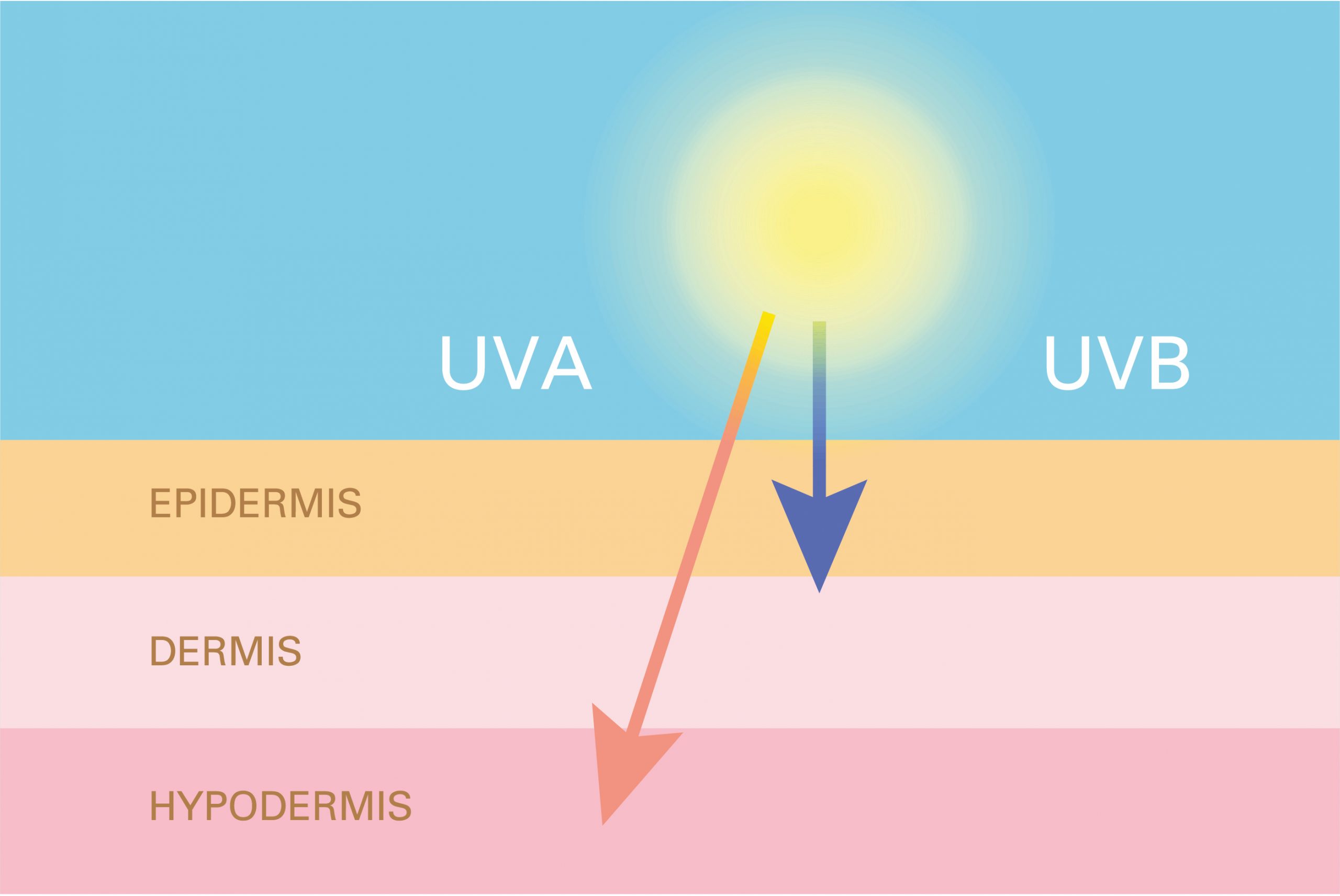
UV-A radiation
As an extension of visible radiation, UV-A radiation is regarded as the least harmful ultraviolet radiation. It Is responsible for tanning.
UV-A radiation penetrates into connective tissue and could cause chronic light damages like premature skin aging and darkening. It also involves in the formation of the free radicals as well as the phototoxic and the photoallergic (solar allergies) reactions. Free radicals are chemical compounds of free electrons, which possess high reactivity and would damage the cells of the epidermis and the dermis. UV-A radiation can also damage paints and plastics.
UV-B radiation
Ranging from 280 to 320nm, UV-B radiation is potentially harmful, as it impedes the growth of the plants. A prolonged exposure to this UV radiation will produce health damage to human beings, such as:
- Very slight damage like sunburn (solar hermit) or more severe damage like DNA mutations in skin cells that may cause skin cancer, since this radiation can be absorbed by the dermal DNA after penetrating into the deepest cell layers of the epidermis.
- Resulting in a less effective immune system. It might increase the risk of infections and decrease the effectiveness of vaccines because UV-B radiation could act as a local immunosuppressive agent to damage Langerhans cells, which play a clear role of antigen presentation in the epidermis.
- Cataracts, pterygium (growth of fibrous tissue on the cornea) and lesions in the retina. It may also increase the risk of other lesions such as cancer of the eyelids and conjunctiva.
Anyone who exposes to a high-energy UV-B rays, may suffer from a form of rapid cellular degeneration because that radiation may break the bonds of the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)-a molecule that encodes an organism’s genetic blueprint.
UV-C radiation
UV-C radiation is the most dangerous radiation among the whole range of ultraviolet rays because it is quite energetic.
Despite all the negative effects that UV radiation produces, a small amount of UV radiation is good for people and is fundamental in vitamin D synthesis; UV radiation is also used for medical purpose, under the health professionals´ supervision, to treat illnesses.

Germiled conclusions
UV-C radiation has been used as a germicide to fight against bacteria, virus, etc., because it is absorbed by DNA to prevent its reproduction. As for the potential risks in relation to the UV-C radiation, we would demand (Not suggest) to choose an ozone-free equipment, which includes a timer and a presence detector, as what we have applied to all of our Germiled models. You can check all the features of our products on our website Germiled .